Here comes another year, and what better way to start your new year than auditing your website’s health with our version of the simplest technical SEO audit guide that even the non-SEOs can understand and implement.
MOZ offers a short checklist created by Geoff Kenyon on how to conduct a technical audit. The items are specifically included in determining why the website is not getting the organic traffic that it deserves. It is also broken down into different categories to make the checking and changing the essential elements of the web design to make it more link-building-friendly.
This technical SEO audit guide is a condensed form of that technical audit.
Before the actual guide, though, here are some necessary information about technical SEO.
What is a technical SEO audit?
Technical SEO audit refers to the process of checking the technical aspects of the site’s search engine optimization (SEO) implementations. The process aims to assess the overall health of the website and discover what fixes are needed to improve its performance on Google and other search engines.
How do you audit a website?
Conducting a technical SEO audit is not without difficulties. There are aspects that you better leave to the SEO experts.
Nonetheless, there are certain technical SEO elements that you can check yourself.
The necessary first step is to log into your Google Search Console and Google Analytics accounts.
Check the indexed pages
Conduct a simple site search on Google incognito.
Put site:https://www.myoptimind.com/ (remove our site’s name and replace it with yours, no spaces), and it will show how many of your pages are currently indexed on Google.
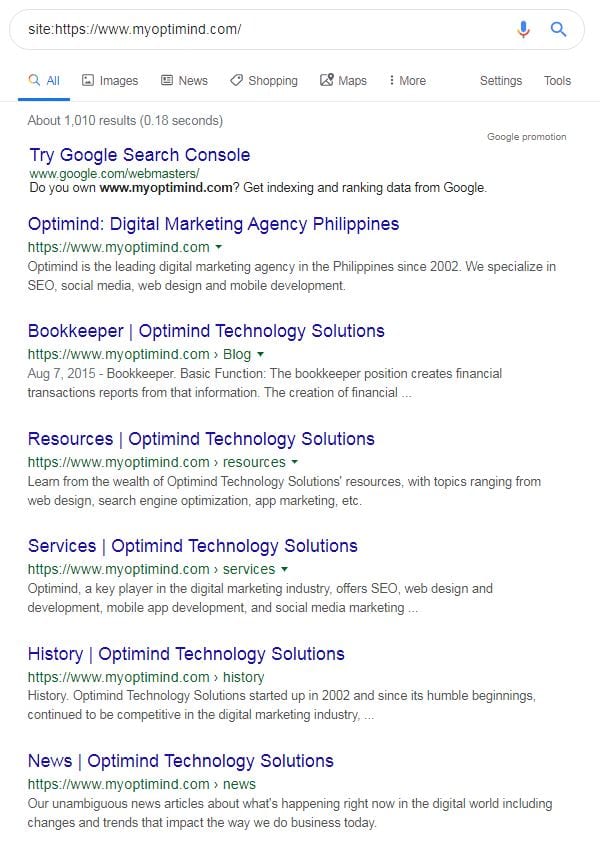
Check the total number of pages Google displayed.
Your homepage should be the first result. There must be some issues (such as a Google penalty if the homepage fails to show on the results page.
Review the total number of organic landing pages
Go to your Google Analytics account.
Count the number of landing pages. Does it match with that of the site: search results? This gives you a good idea of which pages Google deemed valuable to the users.
Search your brand and brand terms
Again, your homepage (i.e., domain name) must be shown first.
Check if the pages being shown are correct. If not, there must be some other issues, such as a Google penalty or improper internal linking.
Review the site architecture.
Check your key pages on Google’s cache
Conduct a simple cache: mywebsite.com.
Are contents showing up or not? Which contents are showing up?
What about navigation links? Are they existing or not? Also, check for links that are not visible on your website.
Examine the text-only version of the cached pages.
Check is the site is mobile responsive
Conduct a mobile-friendly test. Initiate the analysis by putting in your site URL.
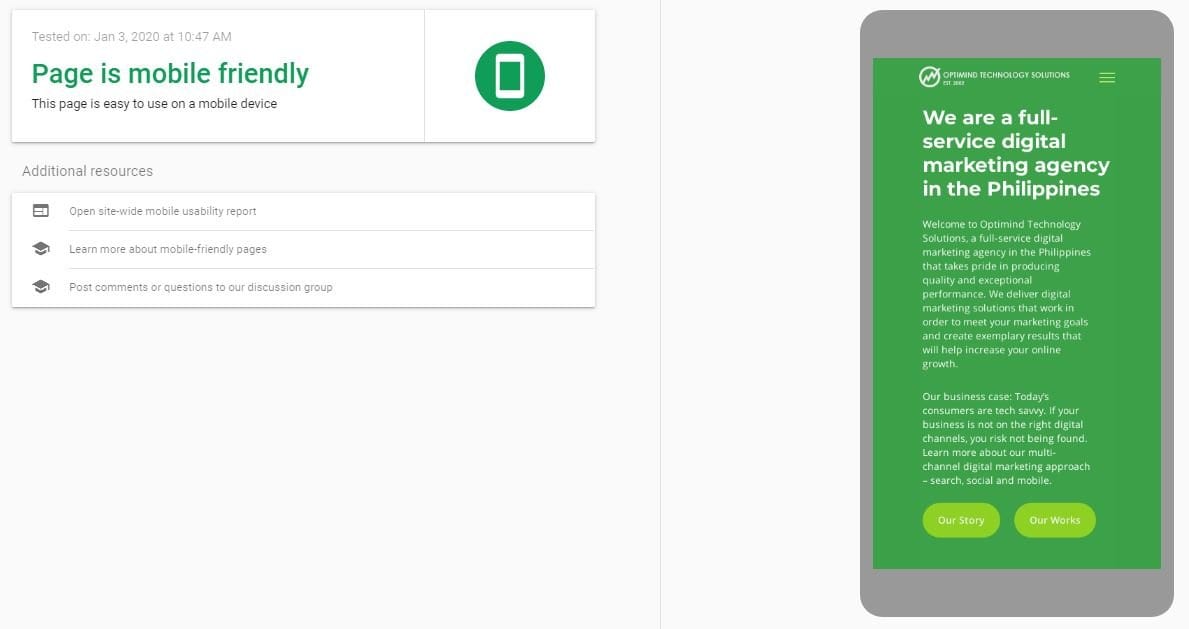
If it is mobile-friendly, conduct a mobile search of your brand and main keywords. Are the landing pages mobile-friendly?
Is Google showing a mobile-friendly label next to your website (that is if it is already mobile-responsive)?
On-page optimization
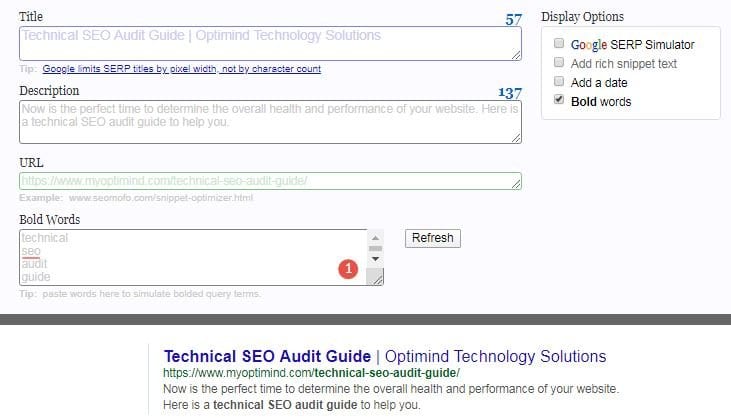
Check if the title tags are optimized
Title tags must be unique and optimized.
Title tags should be between 55 and 60 characters to be fully displayed.
Check how Google displays your title tag.
Review the site if there are missing title tags.
For future implementations, you may use Google’s snippet optimization tool to check how the metadata renders.
Check if the relevant pages are optimized and have meta descriptions
Determine if there are any missing page titles and meta descriptions
Check if the contents have primary keywords or key phrases mentioned organically
The primary keyword must be in the H1 tag.
Are there alternate keywords or key phrases used? Are there variations?
Check if the contents are 100% unique (more on this in the Duplicate content section)
Check the images’ file names and alt text
Do they include the keyword that the page targets?
Check if the URLs are optimized and descriptive
Do you have clean URLs? Are you serving static URLs?
Are the URLs short enough? Shorter URLs say 115 characters, tend to result in better usability.
Content
Check is the homepage content is optimized
Does it contain at least one paragraph? The homepage should contain at least 150 words to explain to the search engine what the page is all about.
Check if the landing pages are optimized
Do they contain two or more paragraphs? Landing pages must be at least 500 words, so search engines would understand what the pages are about.
Are the contents 100% unique, or are they using a template text?
Check if your website contains real, informative and substantial content
Are there pages that contain a list of links?
Did you state verifiable facts or figures?
Are the contents driving the visitors to convert?
Check for proper keyword targeting
Determine if the intent behind the keywords used matches the intent of the landing pages.
Scrutinize the pages for head terms, mid-tail and long-tail keywords, and key phrases. Are there pages that use head terms instead of long-tail keywords?
Check for keyword cannibalization
Conduct a simple mywebsite.com: search for your relevant keywords (e.g., mywebsite.com: search “keyword 1”). Pages that targeted such keyword must appear in the results page.
Check the content formatting
Are the contents correctly and consistently formatted?
Do the contents include the right H tags and images?
Are the contents readable?
Check the heading
Are the headings of your blog posts are well-written? Are they enough to draw the visitors to explore the site further?
Check the ads
Are there any ads above the fold? Remove and replace them with contents.
Duplicate content
Check the URL of each page
Rule of thumb: one URL for each page.
Determine if the URLs include tracking codes or parameters as they result in multiple URLs.
Check for duplicate contents
Check the content snippets by doing a branded search (e.g., mywebsite.com + “Article Title”). There should be one URL showing the snippet.
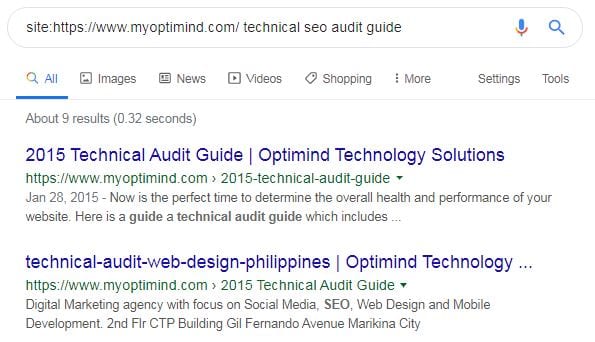
Are there any scraped contents on your site? If there are, ask Google to remove it by filing a removal request.
You may also use Siteliner to find duplicate content within your website.
Review if there are similar contents on sub-domains
If you have multiple domains, check if some of the contents are replicated in those domains.
Check if the contents serve a print-friendly version of the page
These pages also cause duplicate contents.
Check if the contents exist on a secure site version
Make sure that your website is already serving https pages.
Install a valid SSL certificate if your website is not yet on https.
Accessibility and indexation
Check the robots.txt
Go to your website’s robots.txt file.
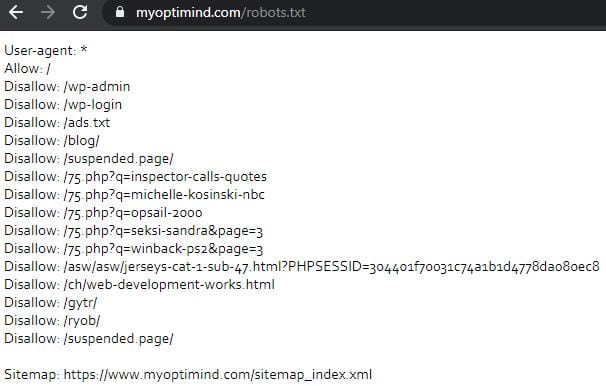
Is the entire site or some of its pages been blocked?
Check the JavaScript, CSS, and cookies
They should be turned off.
Are the contents there?
Are the navigation links workings?
Check for cloaking
Determine how search engines see your website.
Check if 3xx redirects are appropriately used
Determine if the redirects are pointing directly to the final URL. Simply avoid redirect chains.
Scrutinize the website if there are any bad redirects.
Is a canonical version of the site established?
Check for 4xx and 5xx errors
Check the sitemap
Is there an XML sitemap? Did you list the sitemap.xml file in the robots.txt file?
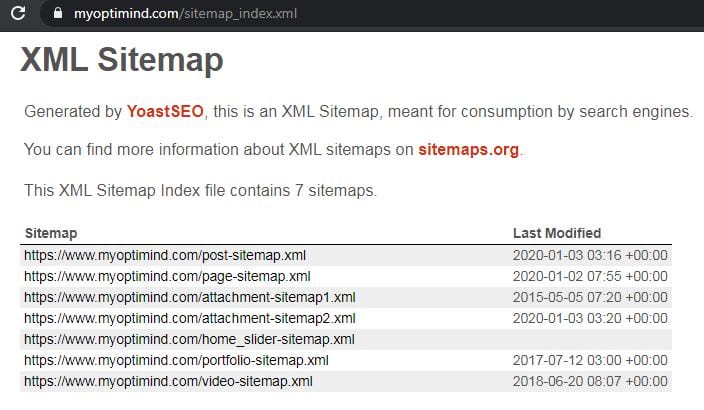
Is it already submitted to Google Webmaster Tools?
If you are using Yoast, it automatically generates a sitemap.xml file for your website.
Check for meta robots noindex tag
Inspect all the pages if they are accidentally tagged with noindex command. They shouldn’t be.
Alternatively, inspect all the pages that should have noindex tags.
Architecture
Check if links are included in the relevant content
Scrutinize whether the anchor texts are relevant to the linked page
Determine the number of links on each page
Rule of thumb: about 100 to 200 links are okay (not a hard rule though).
Strive for under ten links for every page, particularly the high-traffic pages.
Check whether a vertical linking structure exists
Is the homepage linking to category pages? Are category pages linking to sub-category pages appropriately?
Are the product pages linking to the relevant category or sub-category pages?
Check whether a horizontal linking structure exists
Are the category pages linking to other relevant pages?
Are the product pages linking to the relevant category or sub-category pages?
Check for broken links
Technical
Check if the contents are being served in JavaScript
Determine if the contents are being pulled in via iFrames
Check whether the rel canonical link tag is implemented correctly
Scrutinize if your site is using absolute URLs and not relative URLs
Speed
Check the page load time of each page on the site (if possible)
Go to Pagespeed Insights. Put your website URL in the field to initiate the analysis.
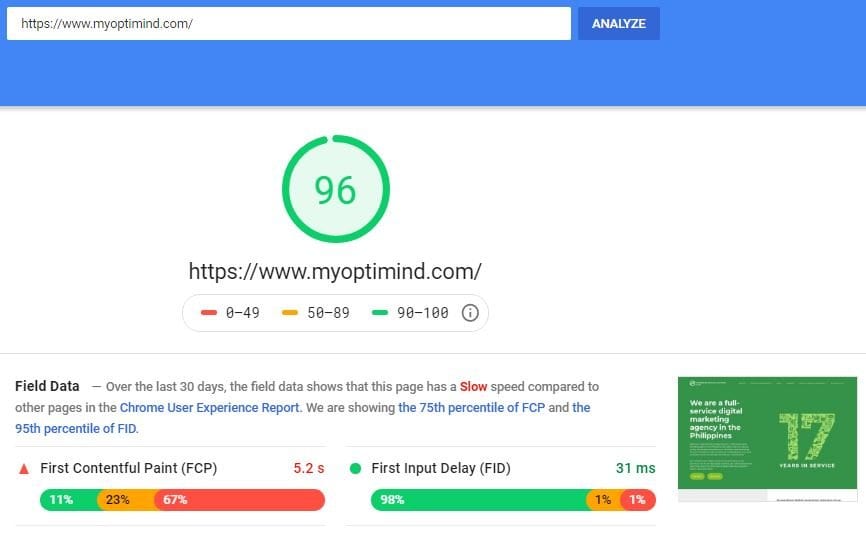
The tool shows fixes below the page speed scores.
Check whether compression is enabled
Inspect if caching is enabled
Check if JavaScript, CSS, and HTML are minified
Determine if the hosting provider is having some issues
Check if the images are optimized for the web
Mobile
Check the synergy between the desktop site and the mobile site
Are proper markups used?
Inspect the mobile experience
Determine if the experience matches the intent of the mobile users.
Check and remove if there are faulty mobile redirects
With this checklist, you will be able to check and correct issues around the main technical elements of your website. The audit will result in solutions to make your site perform better.
If this is too much and too technical a task for you, you may hire specialists to check your site for you. Any specialist can outline the problems of your website and provide detailed recommendations. He can implement the recommended suggestions.
Optimind Technology Solutions offers a free SEO audit (basic). Send us your website URL so you may have a grasp of the overall health of your website.